Creating the GitHub Actions Workflow
In this section, we’ll create the GitHub Actions workflow that syncs your RDS database to Neon.
🚀 Creating the Workflow File
- In your repository, navigate to:
- Click on “Actions”
- Click “New workflow”
- Choose “Configure”
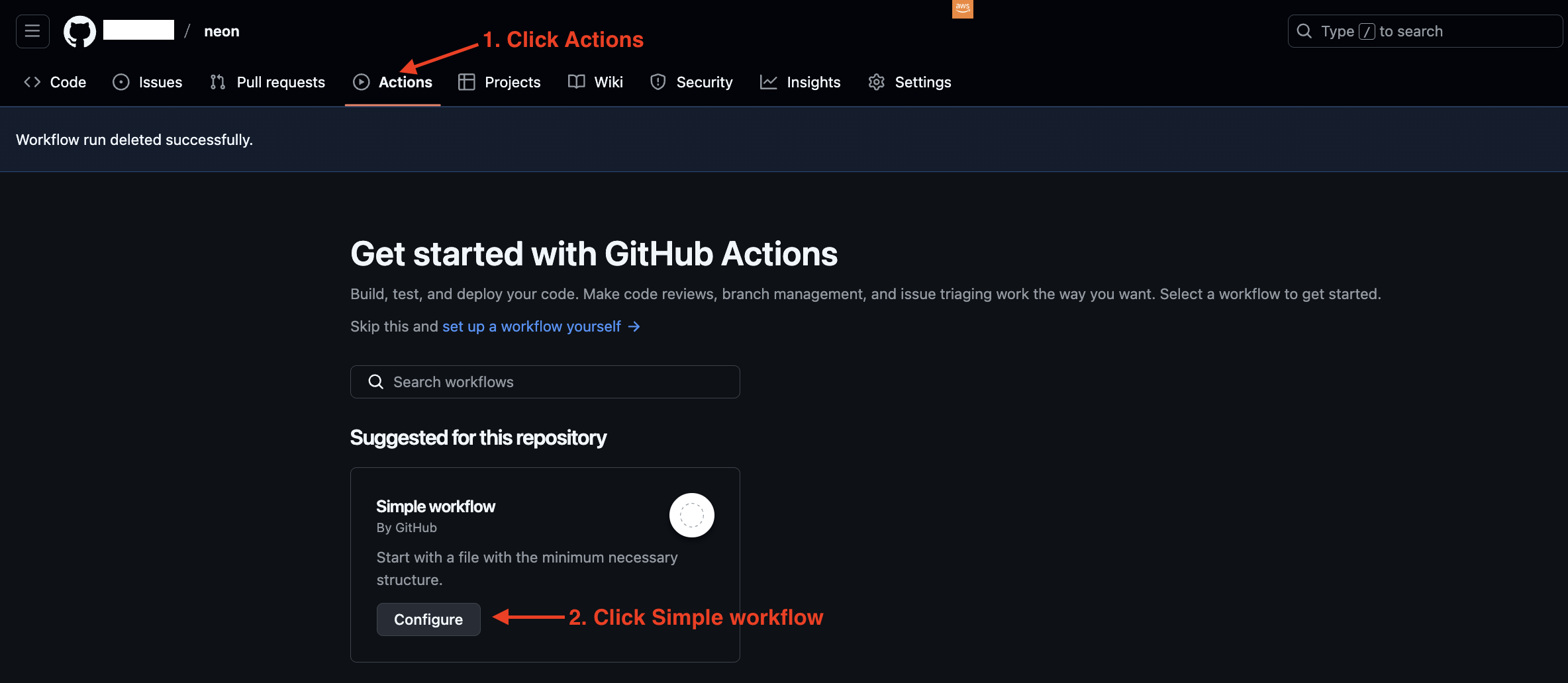
- Name your file
sync.ymland paste the following content:
name: Create Neon Twin
on:
schedule:
- cron: '0 0 * * *' # Runs every day at midnight
workflow_dispatch: # Allows manual trigger
push:
branches: main
permissions:
id-token: write
contents: read
env:
PROD_DATABASE_URL: ${{ secrets.PROD_DATABASE_URL }}
DEV_DATABASE_URL: ${{ secrets.DEV_DATABASE_URL }}
PG_VERSION: '16'
jobs:
dump-and-restore:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Check out repository
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Configure AWS credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v3
with:
role-to-assume: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCOUNT_ROLE }}
aws-region: ${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }}
- name: Verify AWS Identity
run: aws sts get-caller-identity
- name: Get EC2 Instance ID
run: |
# First, let's see all instances with their tags
echo "Checking all instances with VSCodeServer tag..."
aws ec2 describe-instances \
--filters "Name=tag:Name,Values=VSCodeServer" \
--query 'Reservations[*].Instances[*].[InstanceId,Tags[*]]' \
--output json
# Now let's get our specific instance ID
EC2_INSTANCE_ID=$(aws ec2 describe-instances \
--filters "Name=tag:Name,Values=VSCodeServer" \
"Name=instance-state-name,Values=running" \
"Name=tag:aws:cloudformation:stack-name,Values=vscode-server" \
--query "Reservations[0].Instances[0].InstanceId" \
--output text)
echo "Found EC2 Instance ID: $EC2_INSTANCE_ID"
echo "EC2_INSTANCE_ID=$EC2_INSTANCE_ID" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Install Session Manager Plugin
run: |
curl "https://s3.amazonaws.com/session-manager-downloads/plugin/latest/ubuntu_64bit/session-manager-plugin.deb" -o "session-manager-plugin.deb"
sudo dpkg -i session-manager-plugin.deb
rm session-manager-plugin.deb
- name: Check and Install Required Tools
run: |
if ! command -v nc &> /dev/null; then
echo "Installing netcat..."
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y netcat
else
echo "netcat is already installed"
fi
- name: Install PostgreSQL Client
run: |
sudo apt update
yes '' | sudo /usr/share/postgresql-common/pgdg/apt.postgresql.org.sh
sudo apt install -y postgresql-client-${{ env.PG_VERSION }}
- name: Verify PostgreSQL Client Installation
run: |
pg_dump --version
pg_restore --version
- name: Parse DB URL and Start Port Forwarding
run: |
# Parse the PROD_DATABASE_URL
DB_HOST=$(echo $PROD_DATABASE_URL | sed -n 's/.*@\([^:]*\).*/\1/p')
DB_USER=$(echo $PROD_DATABASE_URL | sed -n 's/.*:\/\/\([^:]*\):.*/\1/p')
DB_PASS=$(echo $PROD_DATABASE_URL | sed -n 's/.*:\/\/[^:]*:\([^@]*\).*/\1/p')
DB_NAME=$(echo $PROD_DATABASE_URL | sed -n 's/.*\/\(.*\)/\1/p')
echo "DB_HOST=$DB_HOST" >> $GITHUB_ENV
echo "DB_USER=$DB_USER" >> $GITHUB_ENV
echo "DB_PASS=$DB_PASS" >> $GITHUB_ENV
echo "DB_NAME=$DB_NAME" >> $GITHUB_ENV
# Start SSM session with explicit output to verify
aws ssm start-session \
--target ${{ env.EC2_INSTANCE_ID }} \
--document-name AWS-StartPortForwardingSessionToRemoteHost \
--parameters "{\"host\":[\"$DB_HOST\"],\"portNumber\":[\"5432\"], \"localPortNumber\":[\"15432\"]}" > ssm_output.log 2>&1 &
# Store the SSM process ID
SSM_PID=$!
echo "SSM_PID=$SSM_PID" >> $GITHUB_ENV
# Wait for port forwarding to be established and test the connection
echo "Waiting for port forwarding to be established..."
attempt=1
max_attempts=30
until nc -z localhost 15432 || [ $attempt -gt $max_attempts ]
do
echo "Attempt $attempt of $max_attempts"
cat ssm_output.log
sleep 5
attempt=$((attempt + 1))
done
if [ $attempt -gt $max_attempts ]; then
echo "Failed to establish port forwarding"
cat ssm_output.log
exit 1
fi
echo "Port forwarding successfully established"
ps aux | grep ssm
- name: Dump from RDS
run: |
echo "Dumping data from RDS to file..."
PGPASSWORD=${{ env.DB_PASS }} /usr/lib/postgresql/${{ env.PG_VERSION }}/bin/pg_dump \
-h localhost \
-p 15432 \
-U ${{ env.DB_USER }} \
-d ${{ env.DB_NAME }} \
-Fc -f "${{ github.workspace }}/prod-dump-file.dump"
- name: Restore to Neon
env:
DEV_DATABASE_URL: ${{ secrets.DEV_DATABASE_URL }}
run: |
echo "Restoring data to Neon..."
/usr/lib/postgresql/${{ env.PG_VERSION }}/bin/pg_restore -d "${DEV_DATABASE_URL}" --clean --no-owner --no-acl --if-exists "${{ github.workspace }}/prod-dump-file.dump"
- name: Cleanup
run: |
echo "Cleaning up dump file..."
rm -f "${{ github.workspace }}/prod-dump-file.dump"
# Kill the port forwarding session
pkill -f "ssm start-session"
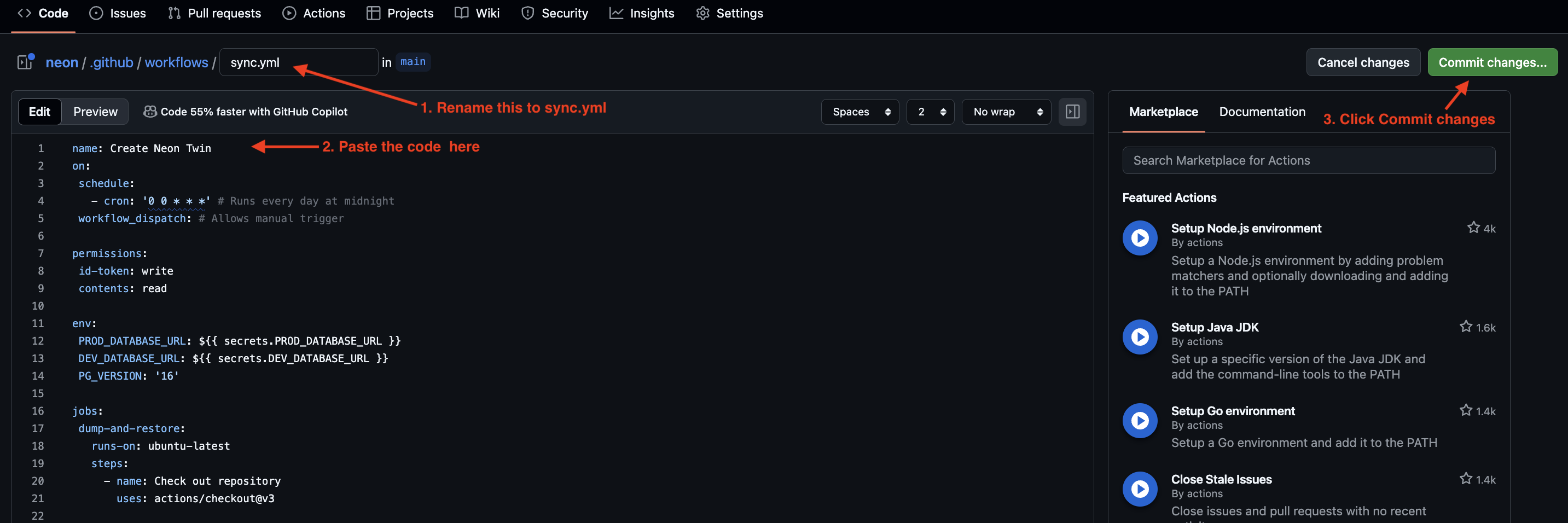
- Click “Commit changes” to save the workflow
🔄 Monitoring the Sync Process
Automatic Initial Sync
When you first commit the workflow file:
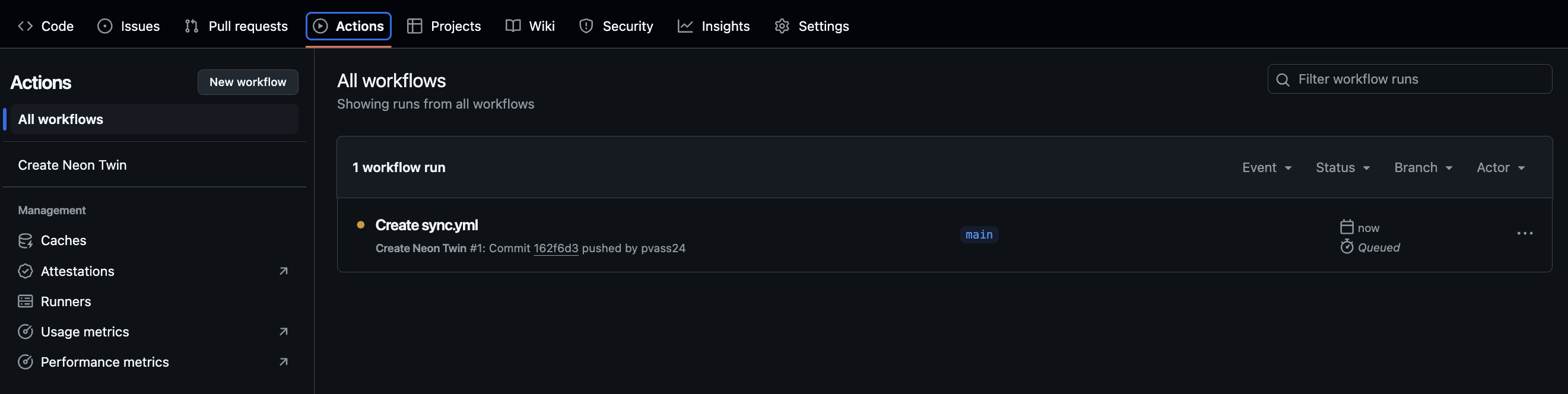
- Navigate to the “Actions” tab in your repository
- You’ll see “Create Neon Twin” workflow starting automatically
- Click on the running workflow to see detailed progress
- This will take about 3-5 mins to complete
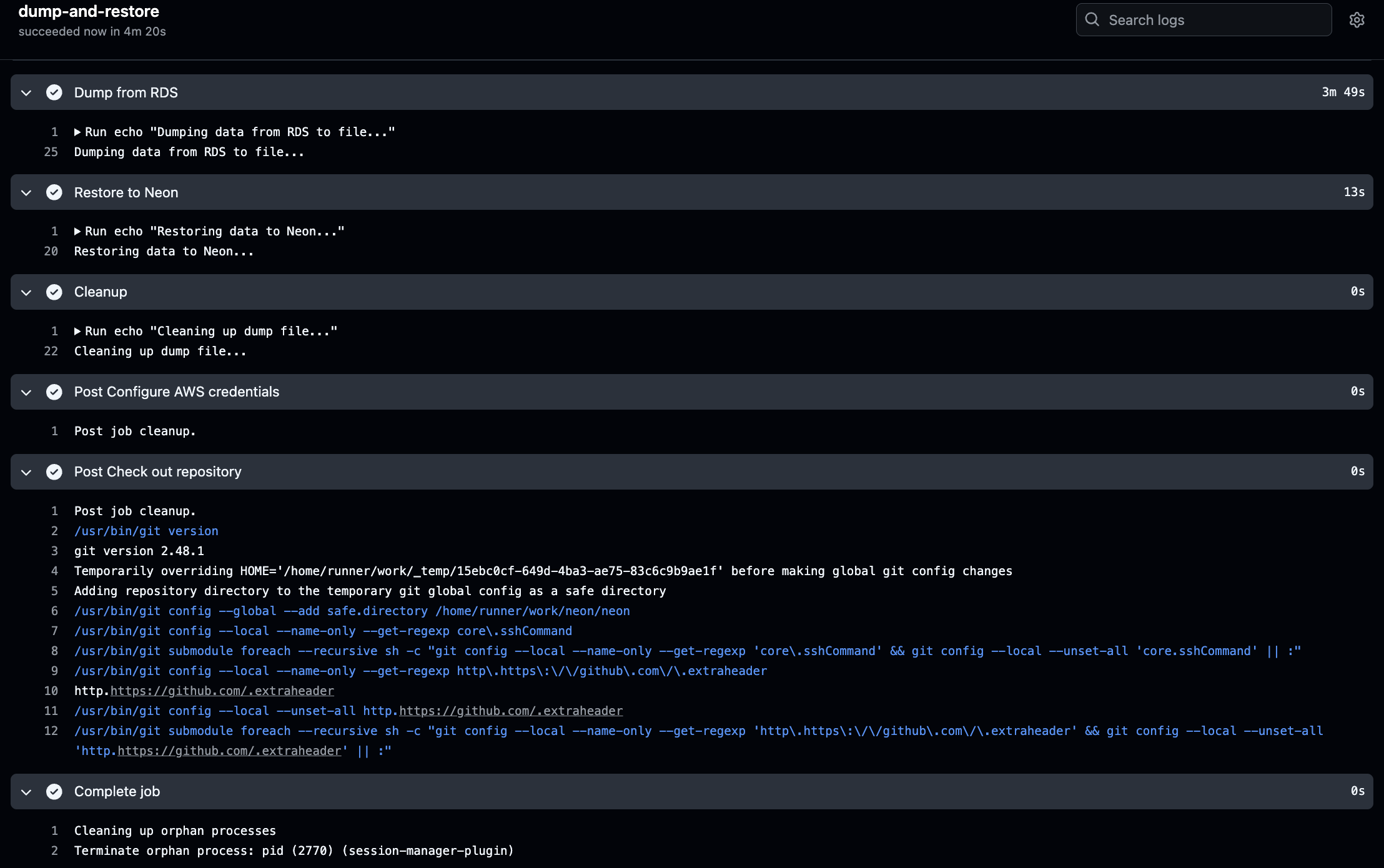
Understanding the Workflow Steps
You can monitor these key stages:
-
AWS Authentication
- Verifies OIDC connection
- Confirms AWS role assumption
-
Database Connection Setup
- Locates VSCode Server instance
- Establishes port forwarding
- You’ll see “Port forwarding established” when successful
-
Data Transfer
- “Dumping data from RDS to file…”
- “Restoring data to Neon…”
- Cleanup process
🎯 Check Neon DB
With your sync configured:
- Verify data in your Neon database
Connect to your Neon database on your VSCode server using the connection string that we set up in earlier steps.
psql $DEV_DATABASE_URL
and run the following query to verify the data:
SELECT d.dept_name, AVG(s.amount) AS average_salary
FROM employees.salary s
JOIN employees.department_employee de ON s.employee_id = de.employee_id
JOIN employees.department d ON de.department_id = d.id
WHERE s.to_date > CURRENT_DATE AND de.to_date > CURRENT_DATE
GROUP BY d.dept_name
ORDER BY average_salary DESC
LIMIT 5;
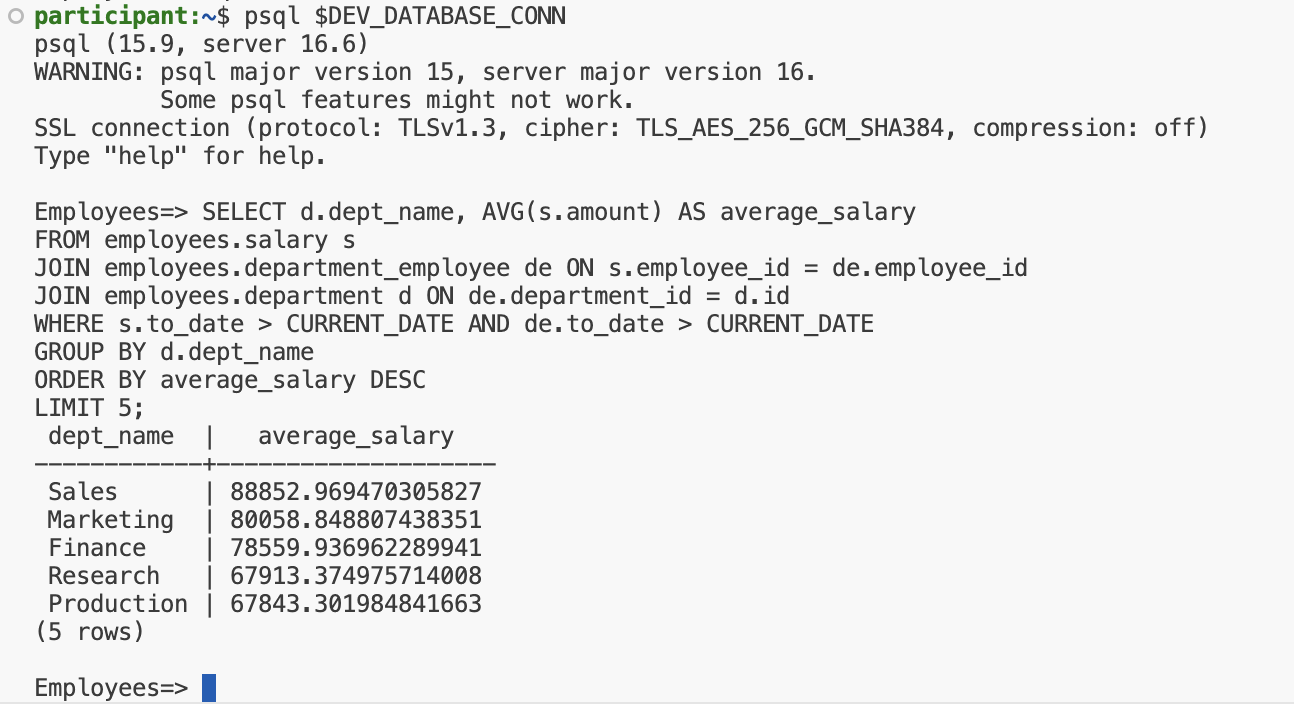
You should see the top 5 departments with the highest average salary.
Exit the database:
\q
🚀 Manual Execution
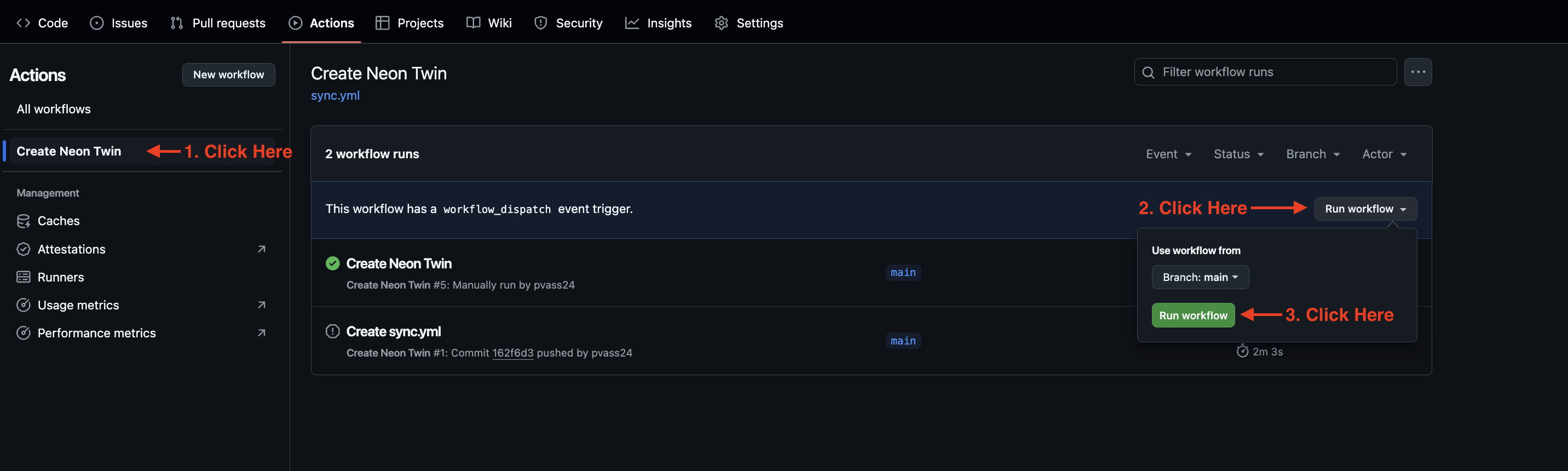
To run the sync manually:
- Go to the “Actions” tab
- Click “Create Neon Twin”
- Select “Run workflow”
- Click the green “Run workflow” button
🔍 Troubleshooting
If you see issues:
- Click on the failed step to expand logs
- Check RDS connection details
- Verify Neon database URL
- Confirm AWS permissions
📅 Scheduled Runs
- The sync runs automatically at midnight daily
- Check “Actions” tab for historical runs
- Each run shows duration and status